What Is a Metal Works Machine? Types, Uses, and Key Features Explained
In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the role of a metal works machine has become increasingly pivotal. These machines not only facilitate the efficient transformation of raw metal materials into finished products but also enhance precision and productivity across various industries. With an array of devices designed for specific functions, understanding the types and features of metal works machines is essential for businesses striving to improve their manufacturing capabilities.
Metal works machines come in various forms, each serving unique purposes ranging from cutting and shaping to welding and finishing. As industries demand higher efficiency and accuracy, the technological advancements in metalworking machines are noteworthy. This overview aims to delve into the different types of metal works machines, explore their uses in various applications, and highlight key features that make them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing. By recognizing the importance of these machines, businesses can better navigate the complexities of metal production and harness the full potential of their operations.

Definition and Functionality of Metal Works Machines
Metal works machines are essential tools used in the metal fabrication industry, designed to shape, cut, and form metal materials into precise components for various applications. These machines include processes such as milling, turning, punching, and welding, making them integral to manufacturing industries, automotive production, and construction. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global metalworking machinery market is expected to reach $110 billion by 2025, demonstrating the growing demand and investment in efficient and advanced machinery.
The functionality of metal works machines extends beyond mere fabrication; they enhance productivity and precision. For instance, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are equipped with software that allows for highly accurate and repeatable performance in shaping metal. This technological advancement reduces human error, leading to increased product quality and efficiency. A study by Grand View Research notes that CNC machines will hold a significant share of the market, reflecting their diverse applicability in various industries.
**Tip:** When selecting a metal works machine, consider the specific type of projects it will be used for. Understanding whether you need a machine for heavy-duty industrial applications or lighter tasks can help streamline operations and maximize investment. Additionally, always evaluate energy efficiency to reduce operational costs in the long run.
Common Types of Metal Works Machines and Their Characteristics
Metal works machines are essential tools in the manufacturing process, facilitating various types of metal fabrication. Common types include lathes, milling machines, and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, each serving distinct purposes yet sharing the common goal of enhancing precision and efficiency in metalworking. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global CNC machine market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for automation and high-precision components across various industries.
Lathes are primarily used for shaping metal by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool, making them ideal for creating cylindrical parts. They come in various types such as engine lathes and turret lathes, each characterized by specific operational features that cater to different manufacturing needs. Milling machines, on the other hand, employ rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, allowing for complex shapes and designs. The versatility of milling machines has played a significant role in boosting production efficiency, as evidenced by their rising adoption rate in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
CNC machines represent a significant advancement in metal working technology, offering automation, superior accuracy, and repeatability. Unlike traditional machines, CNC equipment can execute complex commands from a computer, leading to reduced human error and streamlined processes. The increasing integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology with CNC machines is also reshaping the landscape of metalworking, enabling real-time monitoring and maintenance, which further optimizes productivity and minimizes downtime.
What Is a Metal Works Machine? Types, Uses, and Key Features Explained
| Machine Type | Description | Common Uses | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling Machine | A computer-controlled machine used to shape materials. | Manufacturing parts for electronics, automotive, and aerospace. | Precision control, multiple axes, programmable. |
| Laser Cutting Machine | Uses a laser to cut materials into desired shapes. | Sign making, metal fabrication, custom designs. | High accuracy, speed, and versatility in materials. |
| Press Brake | Forms metal sheets by bending them into specified angles. | Sheet metal forming, structural components. | Adjustable bending angles, programmable back gauge. |
| Metal Lathe | A tool used to shape metal parts by rotation. | Manufacturing cylindrical parts, shafts, and fittings. | Rotating spindle, precision cutting tools, adjustable speeds. |
| Welding Machine | Joins metal pieces together using high heat. | Construction, automotive assembly, repair work. | Types include MIG, TIG, and stick welding; portable options. |
Applications of Metal Works Machines in Various Industries
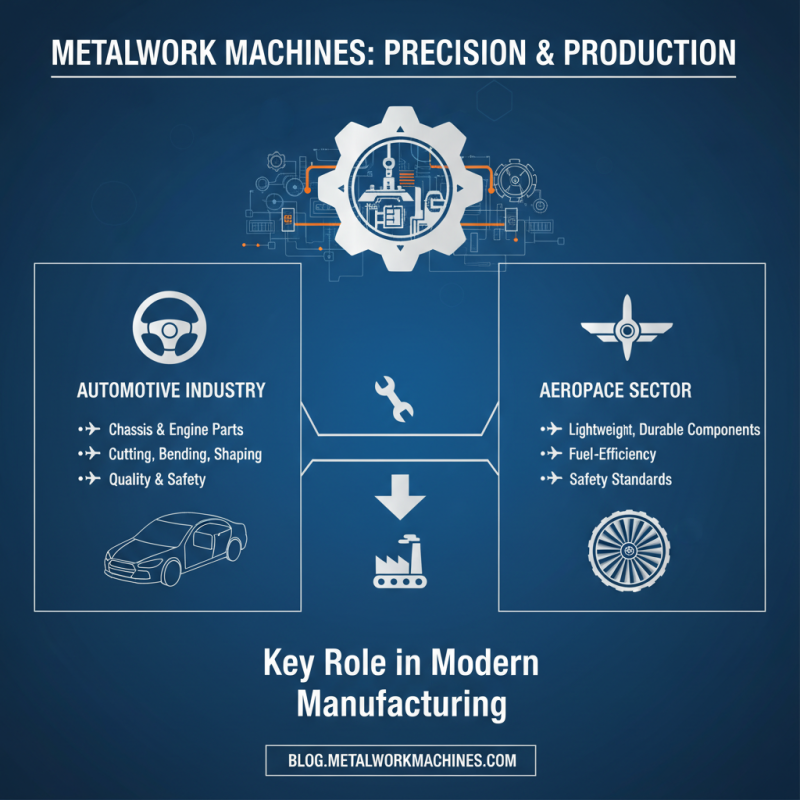
Metal works machines play a crucial role in a variety of industries, enabling precision fabrication and efficient production processes. In the automotive industry, for example, metal works machines are employed for cutting, bending, and shaping components such as chassis and engine parts. This equipment is vital for producing high-quality vehicles that meet strict safety and performance standards. Similarly, the aerospace sector relies on these machines for manufacturing lightweight yet durable components, ensuring that aircraft are both fuel-efficient and safe.
In construction, metal works machines are used for creating structural steel elements that form the backbone of buildings and bridges. These machines facilitate the cutting and welding of steel beams, which are essential for providing stability and support to large structures. Additionally, the electronics industry utilizes these machines for producing enclosures and heatsinks, where precise metal fabrication is necessary for device functionality and thermal management.
Tip: Always ensure that proper safety protocols are followed when operating metal works machines, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and regular maintenance checks to minimize risks associated with malfunctioning equipment. By adhering to safety guidelines, companies can enhance workplace safety and improve productivity.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Metal Works Machine
When selecting a metal works machine, several key features should be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific tasks. First, precision and accuracy are paramount. Machines equipped with advanced control systems can enhance the precision of cuts and finishes, which is crucial in industries where accuracy directly impacts product quality. For instance, CNC machines are often favored for their ability to produce highly detailed components with minimal human intervention.
Another vital consideration is the machine's durability and build quality. Metal works machines are subject to significant wear and stress, so robust materials and engineering can extend their lifespan and reliability. It's essential to assess the construction of the machine, including the frame, components, and any protective features that prevent damage from metal shavings and other debris.
Additionally, evaluate the machine's capability to handle various materials and thicknesses, which determines its versatility and range of applications in your projects. This adaptability is especially important for workshops dealing with diverse metal types and varying production requirements.
Maintenance and Safety Practices for Metal Works Machines
Metal works machines are integral to the manufacturing industry, facilitating the shaping and forming of metal components. However, their operation entails inherent risks, highlighting the importance of maintenance and safety practices. Regular maintenance ensures the machines function optimally and reduces the likelihood of workplace accidents. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), nearly 20% of workplace injuries in manufacturing are due to machine-related accidents. Therefore, implementing a thorough maintenance schedule is not only prudent but essential for safety.
To maximize safety, operators should adhere to specific guidelines before, during, and after using metal works machines. This includes inspecting machines for wear and tear, ensuring all safety guards are in place, and providing proper training for all personnel. Industry reports indicate that companies with robust safety protocols in place can reduce accidents by up to 50%. Additionally, creating a clean and organized workspace minimizes hazards and promotes an efficient workflow.
Tips: Regularly check the alignment of machine parts to prevent malfunctions. Equip all operators with personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety goggles, to mitigate injury risks. Encourage a culture of safety where employees feel empowered to report unsafe conditions or practices without fear, fostering a safer work environment for everyone.